The Importance of Ethernet Switches in Today’s IoT Industry
Ethernet is the most common Local Area Network (LAN) standard in the world. It has evolved dramatically since its first application and today is the standard protocol for IP-based networks and the Internet.
Ethernet is the name for IEEE 802.3 standard based on the Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) protocol, which defines when to transmit and what is to happen if a collision is detected. CSMA/CD also handles endpoint addressing, transmission speeds and the physical media. Ethernet technology is designed to solve the problem of packet collision in a shared network by having network-connected devices follow a set of rules that allow devices to talk to each another without talking over each other. These network-connected devices are physically connected by twisted pair or fiber to an Ethernet switch that then orchestrates the flow of data between devices, applications and the Internet.
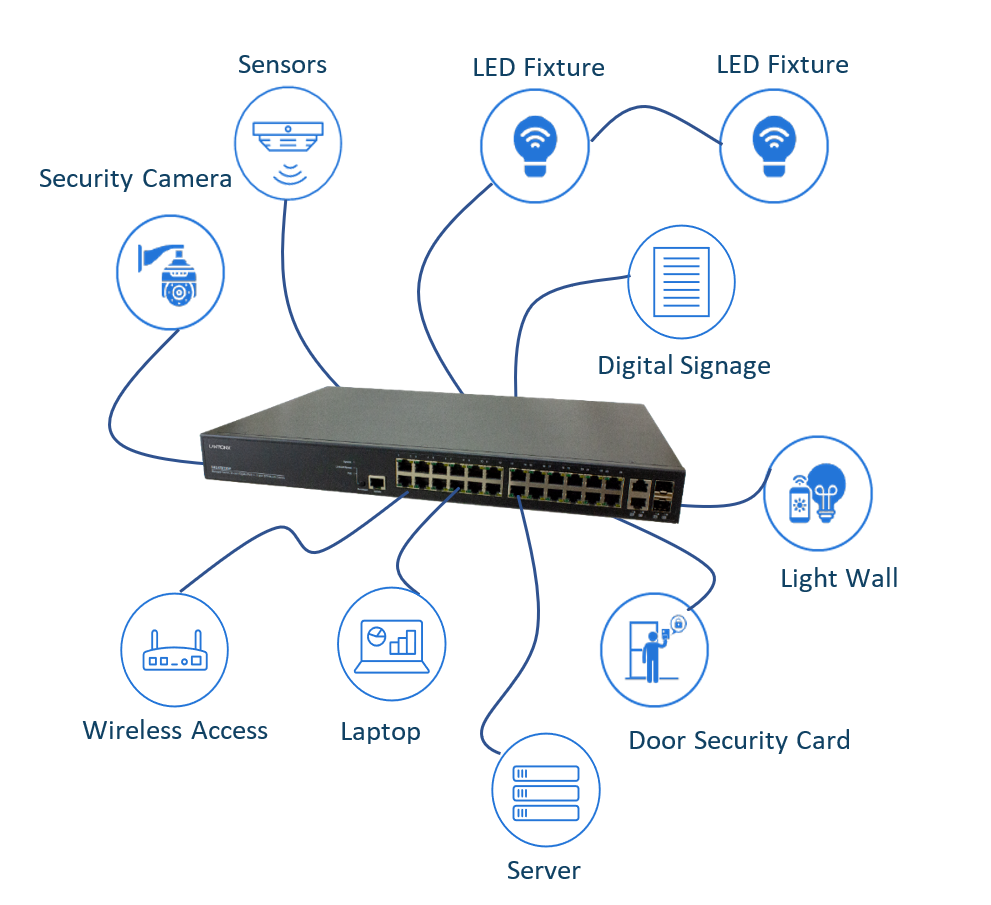
Ethernet switches have also become the common building block technology for most networks. They comprise a common networking device used to connect devices on a LAN, to each other and the Internet. Networking devices on a LAN include computers, printers, servers, Wi-Fi access points, security cameras, PoE lighting and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. These devices are connected to the Ethernet switch via copper or fiber cables.
Industry analysts Dell’Oro Group estimate that campus switch revenue will increase from $18.8 billion in 2022 to $20.7 billion in 2027. Looking at 2023, despite concerns about the challenging macroeconomic environment and a tough comparison with 2022, Dell’Oro Group expects campus switch sales to grow by 3 percent, reaching a new record revenue level by year’s end.
How Ethernet Switches Function
Ethernet operates at the physical and data link level of the OSI reference model.
Ethernet switches connect multiple devices together by physically cabling those devices to the same switch or to devices that are connected to another switch on the same network. These connections are made with twisted pair or fiber cable.
Every Ethernet device has a unique identifier called a media access control (MAC) address. The MAC address is assigned by the manufacturer and is hardcoded to the device. The MAC address is used in the data link layer of the OSI model and cannot be changed.
When Ethernet packets are transmitted to an Ethernet switch, the source device’s MAC address and the port to which it is connected are held in the switch MAC address table. The switch then refers to its MAC address table to see if the destination MAC address is connected to the same switch. If it is, the switch then forwards the packet(s) to the known destination port. If the switch does not recognize the destination MAC address, it will broadcast the packet(s) to all ports on the switch and wait for a response from the destination device.
If the switch is connected directly to the destination device, the device accepts the data packet, responds and completes the transmission. If the device is connected to another switch, the next switch repeats the lookup and forward process until the frame reaches the intended destination.
Summary
Ethernet switches vary in port counts, managed vs unmanaged, hardened vs enterprise, Power over Ethernet (PoE) and other functions. There are switches for specific applications, such as security and surveillance, transportation and smart buildings, as well as access switches, aggregation switches and core switches. The application and requirement determine what type of Ethernet switch is needed.
Since their introduction, Ethernet switches have been essential for enabling network connectivity. Now, Ethernet switches of an even higher importance because of their critical role in making wired and wireless connectivity possible and supporting the growing Internet of Things (IoT).


